Types of Life Insurance: Finding the Right Policy for Your Needs
There are various companies offering different types of life insurance policies. Even the best life insurance companies don’t offer all types of coverage. If you call a typical agency, you’ll only get quotes on a few policy types, primarily term, final expense, and accidental death. But other life insurance types exist that you may have never considered.
We are often asked,
The truth is, there is no one-size-fits-all life insurance policy. Instead, there’s a unique policy tailored for you based on your specific needs, goals, and objectives.
That’s why the “best” policy varies—what works for you may not work for your friend or family member. Let’s explore the different types of life insurance policies available to help you make an informed decision.
Table of Contents
U.S. Life Insurance Market Data
2024 Life Insurance Sales by Type
The most recent data shows the following breakdown of new annualized premium market share and total premium by life insurance type:
| Insurance Type | Market Share (%) | Total New Premium (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Whole Life (WL) | 36% | $5.8 billion |
| Term Life | 19% | $3.0 billion |
| Indexed Universal Life (IUL) | 23–24% | $3.8 billion |
| Variable Universal Life (VUL) | 14–15% | $2.2–$2.4 billion |
| Fixed Universal Life (Fixed UL) | 7% | $1.1 billion |
| Total (all types) | 100% | $15.9–$16.2 billion |
Details by Product Type
- Whole Life (WL): 36% of new premium, $5.8 billion in 2024. This is the lowest market share for WL since 2014, reflecting some shift to other products.[1]
- Term Life: 19% of new premium, just over $3.0 billion in 2024. Policy count increased slightly, up 1%.[2]
- Indexed Universal Life (IUL): 23–24% of new premium, $3.8 billion in 2024. IUL set a new sales record, with policy count growing 10% year over year.[3]
- Variable Universal Life (VUL): 14–15% of new premium, $2.2–$2.4 billion in 2024. VUL saw strong growth, reaching its highest market share since 2006.[4]
- Fixed Universal Life (Fixed UL): 7% of new premium, $1.1 billion in 2024. Policy count fell, but premium grew 7% over the prior year.[5]
Industry Highlights:
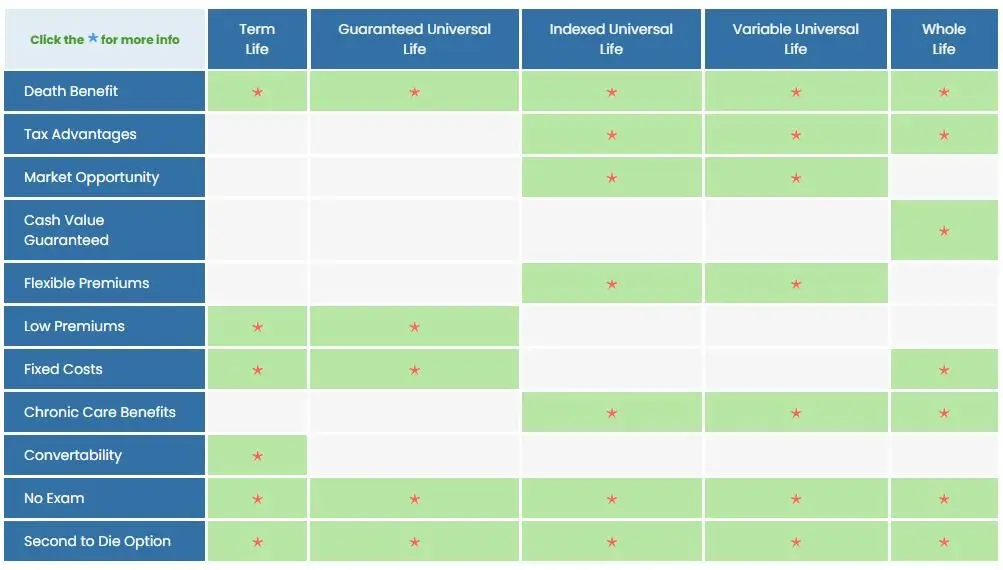
Types of Life Insurance Policies: Term vs. Permanent
Before diving into specific policies, understand there are two primary categories: term life insurance and permanent life insurance. Term provides temporary coverage while permanent offers lifelong protection with added benefits.
Within these categories, policies vary by underwriting requirements, from fully underwritten to no-exam options like accelerated underwriting, simplified issue, and guaranteed issue.
Essential Life Insurance Policy Definitions
Policy
The binding contract between owner and insurer that cannot be canceled by the insurance company except for non-payment. The insured can cancel at anytime.
Owner
The party entering into the legal contract with the insurance company.
Insurer
The company guaranteeing the contract terms (also called carrier). All guarantees depend on the company’s financial strength.
Insured
The individual covered by the policy, often the same person as the owner.
Beneficiary
The person or entity receiving the death benefit upon the insured’s death. There is also the contingent beneficiary and tertiary beneficiary.
Insurance Premiums
Regular payments required to keep the policy active.
Death Benefit
The payout amount going to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death, minus any outstanding policy loans. The death benefit payout can be distributed as a lump sum, interest-only, or over a set period.
Cash Value
The accumulated money in permanent life insurance that can be accessed through policy surrender, withdrawals, or as loan collateral.
Financial Strength Ratings
Ratings from major agencies (A.M. Best, Moody’s, Fitch, S&P) indicating a company’s financial stability. Higher ratings typically mean better capitalization.
Individual vs. Group Life Insurance: Key Differences
Group Life Insurance
- Provided through employers or organizations
- No individual underwriting or medical exam
- Lower premiums (sometimes employer-paid)
- Standard coverage (usually 1-2× your salary)
- Limited customization options
Individual Life Insurance
- Flexible coverage amounts and policy types
- Medical exam requirements (unless qualifying for accelerated underwriting)
- Premiums based on age, health, lifestyle
- Customized to your specific needs
- Portable coverage regardless of employment
Credit Life Insurance: Protecting Your Debts
Credit life insurance pays a death benefit directly to lenders if the borrower dies before paying off a loan. Common examples include mortgage life insurance that protects families from inheriting mortgage debt.
This specialized coverage ensures:
- The lender receives the remaining loan balance
- The debt is settled completely
- Your family is protected from assuming your debts
THE ULTIMATE FREE DOWNLOAD
The Self Banking Blueprint
A Modern Approach To The Infinite Banking Concept

Permanent Life Insurance Policies
Permanent life insurance provides lifelong coverage and builds cash value over time. Unlike term insurance, it doesn’t expire and typically includes both death benefits and living benefits through cash accumulation.
Whole Life Insurance: Reliable Protection with Guarantees
Whole life insurance offers permanent coverage with three key guarantees:
- Guaranteed death benefit that never decreases
- Guaranteed level premium that remains fixed for life
- Guaranteed cash value growth that accumulates tax-deferred
Whole life builds cash value through:
- Regular premium payments
- Paid-up additions that increase your death benefit
- Dividends (in participating policies)
The best dividend-paying whole life policies may produce internal returns exceeding 5% long-term. You can access this cash value through policy loans, using your cash value as collateral rather than withdrawing it directly, which helps avoid tax consequences.
Types of Whole Life Policies:
- Participating policies pay dividends (classified as return of premium, making them tax-free)
- Non-participating policies do not pay dividends
- Limited pay options let you complete payments in a set period (7-Pay, 10-Pay, 20-Pay, to age 65/100)
Universal Life Insurance: Flexible Protection
Universal life insurance offers more flexibility than whole life in two key ways:
- Adjustable premiums let you decide how much goes toward death benefits vs. cash value
- Premium payment flexibility allows you to skip payments if sufficient cash value exists
Universal life’s cash value grows tax-deferred and can be accessed through loans or withdrawals, offering financial flexibility throughout your lifetime.
Guaranteed Universal Life Insurance: Affordable Lifetime Coverage
Guaranteed universal life (GUL) provides lifelong death benefit protection at lower costs than traditional permanent insurance. GUL achieves this by minimizing cash value accumulation.
Key Features:
- No-lapse guarantees ensure coverage continues as long as premiums are paid
- Can be structured to last until specific ages (90, 95, 100, 105, 115, or 121)
- Only GUL to age 121 provides truly permanent coverage
- Lower premiums than whole life insurance
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Market-Linked Growth Potential
Indexed universal life (IUL) links cash value growth to stock market indices like the S&P 500, Nasdaq, or international markets, offering:
- Market-linked returns without direct market investment
- Downside protection through minimum guaranteed floors
- Upside potential limited by participation rates and caps
How IUL Returns Work:
- Participation rate determines what percentage of index gains you receive
- Cap rate limits maximum annual returns
- Floor protects against market losses (typically 0-2%)
THE ULTIMATE FREE DOWNLOAD
The Self Banking Blueprint
A Modern Approach To The Infinite Banking Concept

Variable Life Insurance: Investment-Focused Protection
Variable Universal Life (VUL) combines life insurance with investment opportunities:
- Investment options include fixed accounts and equity-based sub-accounts
- Higher growth potential than traditional policies
- Greater risk exposure due to market volatility
- Minimum death benefit guarantee regardless of investment performance
VUL requires both life insurance and securities licenses to sell due to its investment component. While the death benefit won’t fall below a specified amount, there’s typically no minimum guaranteed cash value.
Asset-Based Long-Term Care Life Insurance: Combined Protection
These asset based hybrid policies combine life insurance with long-term care benefits:
- Death benefit if you die
- Living benefits for qualifying long-term care
- Fixed premiums unlike traditional LTC policies that may increase
- Alternative to standalone long-term care insurance
First-to-Die Life Insurance: Joint Coverage
First-to-die policies cover two people but pay out only after the first person dies, providing:
- Immediate funds for the surviving spouse
- Coverage for funeral costs, debts, and ongoing expenses
- Often more affordable than two separate policies
Survivorship Life Insurance: Estate Planning Tool
Survivorship life insurance (also called second-to-die or joint life) covers multiple individuals with benefits paid:
- Upon the first death (first-to-die configuration)
- Upon the second death (last-to-die configuration)
Advantages include:
- Often less expensive than separate policies
- Less stringent underwriting when one insured is healthier
- Ideal for estate planning and wealth transfer
The Home Ownership Analogy: Term vs. Permanent Life Insurance
Term Life = Renting
- Pay premiums with no equity build-up
- Coverage ends when the term expires
- Rates increase at renewal like rising rent
- All money paid is gone forever
Permanent Life = Owning
- Premium payments build equity (cash value)
- Coverage lasts your entire life
- Cash value grows over time like home equity
- You can access your cash value anytime without bank approval
- Provides both living benefits and death benefits
Term Life Insurance Policies: Temporary Protection
Term life insurance provides pure death benefit protection for a specific period. It’s the most affordable life insurance option, making it popular among younger families seeking income replacement or mortgage protection.
Key Term Life Characteristics
- Pure death protection without cash value
- Lowest initial cost of all insurance types
- Temporary coverage for specified periods
- Becomes expensive with age, often making renewal cost-prohibitive
- 99% of policies expire without paying claims
Level Term Life Insurance: Consistent Premiums
Most term policies feature level premiums for the policy’s duration:
- Fixed premium amounts for 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, or even 40 years
- Stable death benefit throughout the term
- Predictable costs for financial planning
Watch out for “level” term policies that increase rates every five years—always read the fine print.
Convertible Term Life Insurance: Future Flexibility
Convertible term policies allow you to transform your coverage into permanent insurance:
- Convert by the end of the term or a specified age (usually 65-70)
- Convert without proving insurability (no medical exam)
- Convert all or just a portion of your coverage
- Maintain your original health classification
Pro Tip: When shopping for term, consider which permanent policies will be available for conversion later.
Return of Premium Term: Money Back Option
Return of premium (ROP) term refunds your premiums if you outlive the policy:
- Example: $500,000 policy with $5,000 annual premiums for 20 years would return $100,000 if you survive
- Returns are considered return of principal, not earnings (tax-free)
- Higher premiums than standard term policies
- Less common today due to higher costs
Decreasing Term: Mortgage Protection
Decreasing term life features a declining death benefit while premiums remain level:
- Death benefit reduces over time
- Often used to cover mortgage balances
- Coverage terminates when the death benefit reaches zero
- Premiums remain constant despite decreasing coverage
Life Insurance Underwriting Types
Fully Underwritten Policies
Traditional underwriting includes:
- Complete medical exam
- Blood and urine samples
- Height and weight measurements
- Detailed health questionnaire
- Lifestyle questions
Fully underwritten policies typically offer the lowest premiums for healthy applicants.
No Exam Life Insurance Options
No exam life insurance refers to underwriting methods rather than specific policy types. These options include accelerated underwriting and simplified issue coverage.
Some innovative companies like Penn Mutual now offer up to $5 million in no-exam permanent life insurance.
Accelerated Underwriting: Modern Approval Process
Accelerated underwriting combines technology with traditional methods:
- Thorough health and lifestyle application
- Background checks (Medical Information Bureau, prescription database, driving records)
- Potential to skip medical exams for qualified applicants
- Faster approval process (days instead of weeks)
Accelerated underwriting makes permanent insurance more accessible.
Simplified Issue: Streamlined Approval
Simplified issue policies skip the medical exam but include health questions:
- Brief health questionnaire instead of exams
- Higher premiums than fully underwritten policies
- Coverage typically ranges from $25,000 to $250,000
- Faster approval process
Final Expense Insurance: End-of-Life Coverage
Final expense insurance (also called burial insurance) provides small death benefits to cover funeral costs and final expenses:
- Typically purchased by those aged 50-85
- Coverage amounts usually between $5,000 and $25,000
- Simplified underwriting for easier approval
- Available as permanent or term insurance
- Accessible to seniors and those with health issues
Guaranteed Issue Life Insurance: No Questions Asked
Guaranteed issue policies provide coverage with:
- No health questions
- No medical exams
- Guaranteed approval (meeting age/residence requirements)
- Higher premiums due to increased risk
- Limited death benefit in first 2-3 years (graded benefit)
This option is ideal for people with serious health conditions who can’t qualify for other coverage.
Accidental Death Insurance: Limited Coverage
Accidental death policies only cover deaths from accidents:
- Coverage for qualifying accidental deaths only
- Some policies include dismemberment benefits
- Does NOT cover natural causes like cancer, heart disease
- Many exclusions (intoxication, criminal acts)
- Typically inexpensive but limited protection
Conclusion: Finding Your Perfect Life Insurance Policy
The best life insurance policy is the one that meets your unique needs, goals, and objectives. At I&E, we take time to understand your situation and help you navigate these options to find the perfect coverage.
Remember these key points when choosing a policy:
- ✓ Term insurance offers temporary, affordable protection
- ✓ Permanent insurance provides lifelong coverage with living benefits
- ✓ No-exam options make coverage accessible for various health situations
- ✓ The right policy balances cost, coverage, and long-term value
Ready to find your ideal life insurance policy? Contact us today for a complimentary strategy session to discover what insurance solution best fits your needs.
THE ULTIMATE FREE DOWNLOAD
The Self Banking Blueprint
A Modern Approach To The Infinite Banking Concept

Frequently Asked Questions About Life Insurance Types
What’s the difference between term and permanent life insurance?
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific time period (10, 20, or 30 years) and only pays a death benefit. It’s more affordable initially but expires without value if you outlive the term. Permanent life insurance (whole life, universal life) provides lifetime coverage and builds cash value that you can access while living. While more expensive, permanent insurance offers both death benefits and living benefits through its cash value component.
Which type of life insurance builds cash value?
Permanent life insurance policies build cash value, including whole life, universal life, indexed universal life, and variable universal life. Term life insurance does not build cash value. Among permanent policies, whole life offers guaranteed cash value growth, universal life provides flexible premium payments with variable cash accumulation, indexed universal life links cash value to market indices, and variable life allows investment in sub-accounts similar to mutual funds.
What is no exam life insurance and who should consider it?
No exam life insurance allows you to obtain coverage without taking a medical exam. This category includes accelerated underwriting (which uses technology to evaluate health without an exam), simplified issue (which uses a health questionnaire), and guaranteed issue (which requires no health questions). People who should consider no exam policies include those who need coverage quickly, have minor health issues, fear needles, or have been declined for traditional coverage. While convenient, these policies typically offer lower coverage amounts and higher premiums than fully underwritten policies.
What is indexed universal life insurance and how does it work?
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) insurance is a permanent policy that links cash value growth to stock market indices like the S&P 500. It works through three key components: participation rates (determining what percentage of index gains you receive), cap rates (limiting maximum returns), and floors (protecting against market losses, typically 0-2%). This structure allows policyholders to participate in market gains while protecting against market downturns. Unlike directly investing in the market, IUL provides both death benefit protection and market-linked growth potential with downside protection.
What is convertible term life insurance?
Convertible term life insurance is a term policy with an option to convert to permanent coverage (like whole life or universal life) before the term expires or by a specific age (usually 65-70). The key benefit is that you can convert without proving insurability—no medical exam or health questions required. This makes convertible term valuable for those who want affordable coverage now with the flexibility to secure permanent protection later, especially if their health deteriorates. When shopping for convertible term, carefully evaluate which permanent policies will be available for conversion.
What is final expense insurance and who needs it?
Final expense insurance is a specialized policy designed to cover end-of-life costs such as funeral expenses, medical bills, and other debts. Typically offering coverage between $5,000 and $25,000, it’s marketed primarily to people aged 50-85 who may not qualify for traditional coverage due to health issues. These policies feature simplified underwriting with no medical exam and can be either term or permanent. Final expense insurance is ideal for seniors who want to ensure their funeral costs won’t burden their families, those with health conditions that make standard policies unattainable, and individuals who need small coverage amounts for specific end-of-life expenses.
How does guaranteed universal life insurance differ from other universal life policies?
Guaranteed Universal Life (GUL) insurance differs from other universal life policies by focusing on providing lifetime death benefit protection at the lowest possible cost, rather than cash value accumulation. Unlike standard universal or indexed universal life, GUL features include: no-lapse guarantees ensuring coverage continues as long as premiums are paid; minimal cash value growth; lower premiums than whole life; and options to structure coverage to last until specific ages (90, 95, 100, 105, 115, or 121). GUL is ideal for those who want permanent coverage primarily for the death benefit and are less concerned with cash value accumulation.





3 comments
Bonnie LaGambo
Just want to get a price on term life insurance
Insurance&Estates
Hi Bonnie, you can get life insurance quotes for term life and whole life here: https://www.insuranceandestates.com/life-insurance-quotes/
You can also give us a call at 877-787-7558 to speak to a life insurance agent.
Best, Steve Gibbs, for I&E
Steven Gibbs is a licensed insurance agent, and the following agent
license numbers of Steven Gibbs are provided as required by state law:
Resident License; AZ agent #17508301,
Non-resident Licenses: TX agent #2273189, CA agent #0K10610,
LA agent #769583, MA agent #2049963, MN agent #40563357,
UT agent #655544.
BIKRAMJEET BANERJEE
This is Bikramjeet Banerjee a lic insurance advisor from Kolkata gran the information about insurance plans